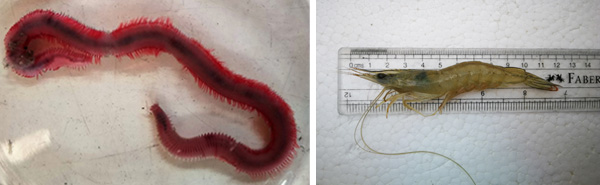
 Researchers tested if giving polychaete mud worms to shrimp along with other foods would affect their reproduction and larval quality. SEAFDEC/AQD Associate Researcher Erish Estante-Superio fed three groups of Indian white shrimp (Penaeus indicus) different diets for 60 days. One group consumed mud worms once a week, another consumed mud worms twice a week, and the control group was not given mud worms. They found that the groups that got mud worms had more frequent and successful spawning than the group that did not. They also found that the offspring of groups that consumed mud worms were more resistant to freshwater stress than the offspring that had no mud worms. They concluded that feeding mud worms to Indian white shrimp, even once a week, can improve their reproductive performance and offspring quality in the hatchery.
Researchers tested if giving polychaete mud worms to shrimp along with other foods would affect their reproduction and larval quality. SEAFDEC/AQD Associate Researcher Erish Estante-Superio fed three groups of Indian white shrimp (Penaeus indicus) different diets for 60 days. One group consumed mud worms once a week, another consumed mud worms twice a week, and the control group was not given mud worms. They found that the groups that got mud worms had more frequent and successful spawning than the group that did not. They also found that the offspring of groups that consumed mud worms were more resistant to freshwater stress than the offspring that had no mud worms. They concluded that feeding mud worms to Indian white shrimp, even once a week, can improve their reproductive performance and offspring quality in the hatchery.
Ms. Superio and her co-authors recently published the results of their study, “Inclusion of live mud polychaete (Marphysa iloiloensis) in the feeding regime improved the hatchery performance of domesticated Indian white shrimp (Penaeus indicus)” in the journal Regional Studies in Marine Science. You may request for a copy of their paper here https://repository.seafdec.org.ph/handle/10862/6421.
 SEAFDEC/AQD Southeast Asian Fisheries Development Center | Aquaculture Department
SEAFDEC/AQD Southeast Asian Fisheries Development Center | Aquaculture Department



